Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| ADIPOR1 |
|---|
|
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ADIPOR1, adiponectin receptor 1, ACDCR1, CGI45, PAQR1, TESBP1A, CGI-45 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 607945; MGI: 1919924; HomoloGene: 69199; GeneCards: ADIPOR1; OMA:ADIPOR1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1q32.1 | Start | 202,940,826 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 202,958,572 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 1|1 E4 | Start | 134,343,116 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 134,361,089 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - blood
- monocyte
- skin of leg
- bone marrow
- skin of abdomen
- islet of Langerhans
- olfactory zone of nasal mucosa
- right lung
- minor salivary glands
- upper lobe of left lung
|
| | Top expressed in | - blood
- granulocyte
- stroma of bone marrow
- knee joint
- fetal liver hematopoietic progenitor cell
- neural layer of retina
- triceps brachii muscle
- atrium
- medial head of gastrocnemius muscle
- ankle
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 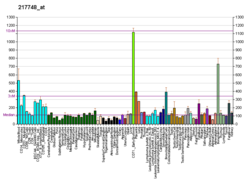 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - adipokinetic hormone receptor activity
- adiponectin binding
- metal ion binding
- identical protein binding
- protein heterodimerization activity
- protein kinase binding
- signaling receptor activity
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- membrane
- intrinsic component of plasma membrane
- plasma membrane
| | Biological process | - glucose homeostasis
- lipid metabolism
- leptin-mediated signaling pathway
- adiponectin-activated signaling pathway
- fatty acid metabolic process
- regulation of lipid metabolic process
- regulation of glucose metabolic process
- negative regulation of cell growth
- fatty acid oxidation
- hormone-mediated signaling pathway
- positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT
- negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT
- negative regulation of epithelial cell migration
- negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling
- G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway
- regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process
- positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001290553
NM_001290557
NM_001290629
NM_015999 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001277482
NP_001277486
NP_001277558
NP_057083 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 202.94 – 202.96 Mb | Chr 1: 134.34 – 134.36 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ADIPOR1 gene.[5] It is a member of the progestin and adipoQ receptor (PAQR) family, and is also known as PAQR1.[6]
Structure
Similar to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), AdipoR1 also possesses 7 transmembrane domains. However, AdipoR1 is orientated oppositely to GPCRs in the membrane (i.e., cytoplasmic N-terminus, extracellular C-terminus) and does not associate with G proteins.[5]
Function
The adiponectin receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, serve as receptors for globular and full-length adiponectin and mediate increased AMPK and PPAR-α ligand activities, as well as fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake by adiponectin.[5][7] In 2016, the University of Tokyo announced that it would launch an investigation into claims of fabrication of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 identification data, as accused by an anonymous person/group called Ordinary_researchers.[8]
Ligands
Agonists
Peptide
Non-peptide
Antagonists
Peptide
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000159346 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026457 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b c Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, et al. (June 2003). "Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects". Nature. 423 (6941): 762–9. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..762Y. doi:10.1038/nature01705. PMID 12802337. S2CID 52860797.
- ^ Tang YT, Hu T, Arterburn M, Boyle B, Bright JM, Emtage PC, et al. (September 2005). "PAQR proteins: a novel membrane receptor family defined by an ancient 7-transmembrane pass motif". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 61 (3): 372–80. Bibcode:2005JMolE..61..372T. doi:10.1007/s00239-004-0375-2. PMID 16044242. S2CID 31473802.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ADIPOR1 adiponectin receptor 1".
- ^ University of Tokyo to investigate data manipulation charges against six prominent research groups ScienceInsider, Dennis Normile, Sep 20, 2016
- ^ a b c Otvos L, Knappe D, Hoffmann R, Kovalszky I, Olah J, Hewitson TD, et al. (2014). "Development of second generation peptides modulating cellular adiponectin receptor responses". Frontiers in Chemistry. 2: 93. Bibcode:2014FrCh....2...93O. doi:10.3389/fchem.2014.00093. PMC 4201147. PMID 25368867.
- ^ Okada-Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Iwabu M, Honma T, Hamagami K, Matsuda K, et al. (November 2013). "A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity". Nature. 503 (7477): 493–9. Bibcode:2013Natur.503..493O. doi:10.1038/nature12656. PMID 24172895. S2CID 4447039.
- ^ a b c d Sun Y, Zang Z, Zhong L, Wu M, Su Q, Gao X, et al. (2013). "Identification of adiponectin receptor agonist utilizing a fluorescence polarization based high throughput assay". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e63354. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...863354S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063354. PMC 3653934. PMID 23691032.
External links
Further reading
- Crimmins NA, Martin LJ (September 2007). "Polymorphisms in adiponectin receptor genes ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 and insulin resistance". Obesity Reviews. 8 (5): 419–23. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00348.x. PMID 17716299. S2CID 825474.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Lai CH, Chou CY, Ch'ang LY, Liu CS, Lin W (May 2000). "Identification of novel human genes evolutionarily conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans by comparative proteomics". Genome Research. 10 (5): 703–13. doi:10.1101/gr.10.5.703. PMC 310876. PMID 10810093.
- Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S, et al. (June 2003). "Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects". Nature. 423 (6941): 762–9. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..762Y. doi:10.1038/nature01705. PMID 12802337. S2CID 52860797.
- Kharroubi I, Rasschaert J, Eizirik DL, Cnop M (December 2003). "Expression of adiponectin receptors in pancreatic beta cells". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 312 (4): 1118–22. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.042. PMID 14651988.
- Civitarese AE, Jenkinson CP, Richardson D, Bajaj M, Cusi K, Kashyap S, et al. (May 2004). "Adiponectin receptors gene expression and insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic Mexican Americans with or without a family history of Type 2 diabetes". Diabetologia. 47 (5): 816–20. doi:10.1007/s00125-004-1359-x. PMID 15105989.
- Wang H, Zhang H, Jia Y, Zhang Z, Craig R, Wang X, et al. (August 2004). "Adiponectin receptor 1 gene (ADIPOR1) as a candidate for type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance". Diabetes. 53 (8): 2132–6. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.8.2132. PMID 15277397.
- Staiger H, Kaltenbach S, Staiger K, Stefan N, Fritsche A, Guirguis A, et al. (September 2004). "Expression of adiponectin receptor mRNA in human skeletal muscle cells is related to in vivo parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism". Diabetes. 53 (9): 2195–201. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.9.2195. PMID 15331527.
- Berner HS, Lyngstadaas SP, Spahr A, Monjo M, Thommesen L, Drevon CA, et al. (October 2004). "Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells". Bone. 35 (4): 842–9. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2004.06.008. PMID 15454091.
- Punyadeera C, Zorenc AH, Koopman R, McAinch AJ, Smit E, Manders R, et al. (March 2005). "The effects of exercise and adipose tissue lipolysis on plasma adiponectin concentration and adiponectin receptor expression in human skeletal muscle". European Journal of Endocrinology. 152 (3): 427–36. doi:10.1530/eje.1.01872. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30008881. PMID 15757860.
- Hara K, Horikoshi M, Kitazato H, Yamauchi T, Ito C, Noda M, et al. (July 2005). "Absence of an association between the polymorphisms in the genes encoding adiponectin receptors and type 2 diabetes". Diabetologia. 48 (7): 1307–14. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-1806-3. PMID 15918014.
- Damcott CM, Ott SH, Pollin TI, Reinhart LJ, Wang J, O'connell JR, et al. (July 2005). "Genetic variation in adiponectin receptor 1 and adiponectin receptor 2 is associated with type 2 diabetes in the Old Order Amish". Diabetes. 54 (7): 2245–50. doi:10.2337/diabetes.54.7.2245. PMID 15983228.
- Neumeier M, Weigert J, Schäffler A, Weiss T, Kirchner S, Laberer S, et al. (September 2005). "Regulation of adiponectin receptor 1 in human hepatocytes by agonists of nuclear receptors". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 334 (3): 924–9. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.187. PMID 16023994.
- Zhang J, Holt H, Wang C, Hadid OH, Byrne CD (August 2005). "Expression of AdipoR1 in vivo in skeletal muscle is independently associated with measures of truncal obesity in middle-aged caucasian men". Diabetes Care. 28 (8): 2058–60. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.8.2058. PMID 16043761.
- Tang YT, Hu T, Arterburn M, Boyle B, Bright JM, Emtage PC, et al. (September 2005). "PAQR proteins: a novel membrane receptor family defined by an ancient 7-transmembrane pass motif". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 61 (3): 372–80. Bibcode:2005JMolE..61..372T. doi:10.1007/s00239-004-0375-2. PMID 16044242. S2CID 31473802.
- Jonsson JR, Moschen AR, Hickman IJ, Richardson MM, Kaser S, Clouston AD, et al. (December 2005). "Adiponectin and its receptors in patients with chronic hepatitis C". Journal of Hepatology. 43 (6): 929–36. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.05.030. PMID 16139921.
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 1 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |



















