Black flying fox
| Black flying fox | |
|---|---|
 | |
Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Pteropodidae |
| Genus: | Pteropus |
| Species: | P. alecto |
| Binomial name | |
| Pteropus alecto Temminck, 1837 | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
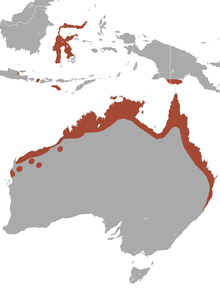 | |
| Black flying fox range | |

Problems playing this file? See media help.
The black flying fox or black fruit bat (Pteropus alecto) is a bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is among the largest bats in the world, but is considerably smaller than the largest species in its genus, Pteropus. The black flying fox is native to Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia. It is not a threatened species.
Taxonomy
Juvenile specimens of this species from Moa Island in Torres Strait have been described as a separate species, Pteropus banakrisi.[2] This supposed species was known as the "Torresian flying fox" or "Moa Island fruit bat".
Description
The black flying fox has short, black hair with a contrasting reddish-brown mantle, and a mean forearm length of 164 mm (6.46 in) and a mean weight of 710 g (1.57 lb). It is one of the largest bat species in the world, and has a wingspan of more than 1 metre (39 in).
Distribution
Black flying foxes are native to Australia (New South Wales, Queensland, Northern Territory and Western Australia), Papua New Guinea (Western Province) and Indonesia (West Papua, Sulawesi, Sumba, and Savu).
Roosting habits
During the day, individuals reside in large roosts (colonies or 'camps') consisting of hundreds to tens of thousands of individuals. They sometimes share their roosts with the grey-headed flying fox (Pteropus poliocephalus), the spectacled flying fox (P. conspicillatus), and/or the little red flying fox (P. scapulatus). They roost in mangroves, paperbark swamps, patches of rainforest and bamboo forests, and very rarely in caves or underneath overhangs.
Reproduction
Black flying foxes breed once a year. A single young is born and carried by its mother for the first month of life, after which it is left behind in the roost when the mother is out foraging at night.
Diet

Black flying foxes eat pollen and nectar from native eucalyptus, lilypillies, paperbark, and turpentine trees. When native foods are scarce, particularly during drought, the bats may take introduced or commercial fruits, such as mangos and apples. This species had been known to travel up to 50 km (31 mi) a night in search of food. In residential areas, the species has adapted to eating introduced cocos palm trees as a substitute for scarcer native species - and now accounts for around 30% of the animals' food source. However, the high acidity of the palm fruits can prove toxic and may lead to death.[3]
Conservation

The black flying fox is not listed as threatened on the IUCN Red List; nevertheless, the species is exposed to several threats, including loss of foraging and roosting habitat, and mass die-offs caused by extreme temperature events.[4] Because climate change is predicted to make Australia hotter, the negative impacts this species faces from extreme temperature events are expected to grow into a larger problem.[5] According to one study, these animals begin to die once temperatures reach above 40°C.[5] Another study of records from wildlife rehabilitation clinics in Australia found that heat stress particularly affected black flying foxes compared to other flying fox species. Clinic records indicated that 46% of wildlife rescues of black flying foxes were due to heat stress, compared to 18% of grey-headed flying fox rescues and 8% of little red flying fox rescues.[6]
When present in urban environments, black flying foxes are sometimes perceived as a nuisance. Because their roosting and foraging habits bring the species into conflict with humans, it suffers from direct killing of animals in orchards and harassment and destruction of roosts. In Indonesia, this species is frequently consumed as bushmeat, with concerns that the population loss might not be sustainable.[7]
As a disease vector
Negative public perception of the species has intensified with the discovery of three recently emerged zoonotic viruses that are potentially fatal to humans: Australian bat lyssavirus,[8] Hendra virus, and Menangle virus. However, only the Australian bat lyssavirus is known from two isolated cases to be directly transmissible from bats to humans.
Wildlife rescue
Flying foxes often come to the attention of Australian wildlife care and rescue organisations, such as Wildcare Australia,[9] Orphan Native Animal Rear and Release Association Incorporated,[10] Wildlife Carers Darling Downs, Bat Care, Bat Rescue, Tweed Valley Wildlife Carers, and WIRES when reported as injured, sick, orphaned or abandoned. A very high proportion of adult flying fox injuries are caused by entanglement in barbed wire fences or loose, improperly erected fruit tree netting, both of which can result in very serious injuries and a slow, agonizing death for the animal if not rescued quickly.
References
- ^ Roberts, B.; Eby, P.; Tsang, S.M.; Sheherazade (2017). "Pteropus alecto". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T18715A22080057. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T18715A22080057.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Helgen, Kristofer M. (2004), "On the Identity of Flying-Foxes, genus Pteropus (Mammalia: Chiroptera), from Islands in the Torres Strait, Australia." Zootaxa 780:1–14.
- ^ "Remove Cocos to deter flying foxes". Queensland Times. 15 July 2013. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
- ^ Australian flying fox die-offs
- ^ a b Welbergen, Justin A; Klose, Stefan M; Markus, Nicola; Eby, Peggy (2007-11-28). "Climate change and the effects of temperature extremes on Australian flying-foxes". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 275 (1633): 419–425. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1385. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2596826. PMID 18048286.
- ^ Mo, Matthew; Roache, Mike; Haering, Ron; Kwok, Alan (2021). "Using wildlife carer records to identify patterns in flying-fox rescues: a case study in New South Wales, Australia". Pacific Conservation Biology. 27 (1): 61. doi:10.1071/pc20031. ISSN 1038-2097. S2CID 225528523.
- ^ Mickleburgh, S., Waylen, K., & Racey, P. (2009). Bats as bushmeat: a global review. Oryx, 43(02), 217-234.
- ^ "Australian Bat Lyssavirus Infection in a Captive Juvenile Black Flying-Fox". Field, H. and McCall, Bradley J. and Barrett, J. (1999). Emerging Infectious Diseases, 5 (3).[1]
- ^ "Wildcare Australia Inc". Retrieved January 11, 2013.
- ^ "An Introduction to O.N.A.R.R." O.N.A.R.R. Retrieved January 11, 2013.
Further reading
- Hall, Linnea Suzanne & Richards, Gregory C. (2000). Flying-foxes: fruit and blossom bats of Australia. Sydney: University of New South Wales Press. ISBN 0-86840-561-2.
- Markus, Nicola (2002). "Behaviour of the black flying-fox Pteropus alecto: 2. Territoriality and courtship". Acta Chiropterologica. 4 (2): 153–166. doi:10.3161/001.004.0204. S2CID 86125017.
- Markus, Nicola & Blackshaw, Judith K. (2002). "Behaviour of the black flying-fox, Pteropus alecto: 1. An ethogram of behaviour, and preliminary characterisation of mother-infant interactions". Acta Chiropterologica. 4 (2): 137–152. doi:10.3161/001.004.0203. S2CID 86200967.
- Speare, Rick, et al. (1997). "Australian bat lyssavirus infection in three fruit bats from north Queensland." Comm Dis Intell 1997; 21:117-120. Downloadable pdf at: [2]
- Vardon, M.; C. Tidemann (1998). "Reproduction, growth and maturity in the black flying-fox, Pteropus alecto (Megachiroptera: Pteropodidae)". Australian Journal of Zoology. 46 (4): 329–344. doi:10.1071/ZO98023.
- Vardon, M.; C. Tidemann (2000). "The black flying-fox (Pteropus alecto) in north Australia: juvenile mortality and longevity". Australian Journal of Zoology. 48: 91–97. doi:10.1071/ZO99060.
- Welbergen, J.; Klose, S.; Markus, N.; Eby, P. (2008). "Climate change and the effects of temperature extremes on Australian flying-foxes". Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 275 (1633): 419–425. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1385. PMC 2596826. PMID 18048286.
- Welbergen, J. (2008). "Variation in twilight predicts the duration of the evening emergence of fruit bats from a mixed-species roost". Animal Behaviour. 75 (4): 1543–1550. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2007.10.007. S2CID 53170754.
External links


- ARKive - images and movies of the black flying-fox (Pteropus alecto)
- Brief history of Megachiroptera / Megabats
- v
- t
- e
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Infraclass: Eutheria
- Superorder: Laurasiatheria
- Order: Chiroptera
Subfamily Nyctimeninae | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
Subfamily Cynopterinae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subfamily Harpyionycterinae | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
Subfamily Macroglossinae | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
Subfamily Pteropodinae | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
Subfamily Rousettinae | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
Subfamily Epomophorinae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||











