Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C7H4FeO3 |
| Molar mass | 191.951 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale yellow oil |
| Boiling point | 47 °C (117 °F; 320 K) 3 mm |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
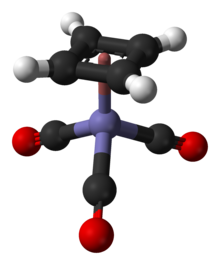
Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl is an organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C4H4)(CO)3. It is a yellow oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It has been used in organic chemistry as a precursor for cyclobutadiene, which is an elusive species in the free state.[1]
Preparation and structure
Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl was first prepared in 1965 by Pettit from 3,4-dichlorocyclobutene and diiron nonacarbonyl:[2][3]
- C4H4Cl2 + 2 Fe2(CO)9 → (C4H4)Fe(CO)3 + 2 Fe(CO)5 + 5 CO + FeCl2
The compound is an example of a piano stool complex. The C-C distances are 1.426 Å.[4]
Properties
Oxidative decomplexation of cyclobutadiene is achieved by treating the tricarbonyl complex with ceric ammonium nitrate. The released cyclobutadiene is trapped with a quinone, which functions as a dienophile.[5]
Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl displays aromaticity as evidenced by some of its reactions, which can be classified as electrophilic aromatic substitution:[6]
It undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with acetyl chloride and aluminium chloride to give the acyl derivative 2, with formaldehyde and hydrochloric acid to the chloromethyl derivative 3, in a Vilsmeier-Haack reaction with N-methylformanilide and phosphorus oxychloride to the formyl 4, and in a Mannich reaction to amine derivative 5.
The reaction mechanism is identical to that of EAS:
Related compounds
Several years before Petit's work, (C4Ph4)Fe(CO)3 had been prepared from the reaction of iron carbonyl and diphenylacetylene.[7]
(Butadiene)iron tricarbonyl is isoelectronic with cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl.
History
In 1956, Longuet-Higgins and Orgel[8] predicted the existence of transition-metal cyclobutadiene complexes, in which the degenerate eg orbital of cyclobutadiene has the correct symmetry for π interaction with the dxz and dyz orbitals of the proper metal. The compound was synthesized three years after the prediction[9] This case of theory before experiment.[10]
References
- ^ Seyferth, Dietmar (2003). "(Cyclobutadiene)iron Tricarbonyl. A Case of Theory before Experiment". Organometallics. 22: 2–20. doi:10.1021/om020946c.
- ^ Cyclobutadiene- and Benzocyclobutadiene-Iron Tricarbonyl Complexes G. F. Emerson, L. Watts, R. Pettit; J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1965; 87(1); 131-133. First Page
- ^ Pettit, R.; Henery, J. (1970). "Cyclobutadieneiron Tricarbonyl". Organic Syntheses. 50: 21. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.050.0021.
- ^ P. D. Harvey; W. P. Schaefer; H. B. Gray; D. F. R. Gilson; I. S. Butler (1988). "Structure of tricarbonyl(η4-cyclobutadienyl)iron(0) at −45 °C". Inorg. Chem. 27 (1): 57–59. doi:10.1021/ic00274a013.
- ^ L. Brener; J. S. Mckennis; R. Pettit (1976). "Cyclobutadiene In Synthesis: endo-Tricyclo[4.4.0.02,5]deca-3,8-diene-7,10-dione". Org. Synth. 55: 43. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.055.0043.
- ^ Cyclobutadieneiron Tricarbonyl. A New Aromatic System J. D. Fitzpatrick, L. Watts, G. F. Emerson, R. Pettit J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1965, vol. 87, 3254-3255 Abstract
- ^ R. P. Dodge, V. Schomaker, "Crystal Structure of Tetraphenylcyclobutadiene Iron Tricarbonyl", Nature 1960, vol. 186, 798-799.doi:10.1038/186798b0
- ^ Longuet-Higgins, H. C.; Orgel, L. E. (1956-01-01). "385. The possible existence of transition-metal complexes of cyclobutadiene". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 1969–1972. doi:10.1039/JR9560001969. ISSN 0368-1769.
- ^ Criegee, R.; Schröder, G. (1959-01-21). "Ein Nickel-Komplex des Tetramethyl-Cyclobutadiens". Angewandte Chemie (in German). 71 (2): 70–71. doi:10.1002/ange.19590710210.
- ^ Seyferth, Dietmar (2003-01-01). "(Cyclobutadiene)iron TricarbonylA Case of Theory before Experiment". Organometallics. 22 (1): 2–20. doi:10.1021/om020946c. ISSN 0276-7333.
- v
- t
- e
- H2Fe(CO)4
- Na2Fe(CO)4
- Fe(CO)5
- Fe2(CO)9
- Fe3(CO)12
- Fe(CO)3CH3COC2H2C6H6
- FeH
| Organoiron(I) compounds |
|---|
- Fe3C
- FeH2
- Mg2FeH6
- FeF2
- FeCl2
- Fe(ClO4)2
- FeBr2
- FeI2
- FeO
- Fe(OH)2
- FeS
- FeSO4
- (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O
- FeSe
- FeSeO4
- Fe(NO3)2
- Fe3(PO4)2
- FeSi2
- Fe(BF4)2
- FeCr2O4
- FeMoO4
- FeTiO3
- FeCO3
- FeC2O4
- Fe(C2H3O2)2
- Fe(C3H5O3)2
- FeC6H6O7
- FeC12H22O14
- FeI2(CO)4
| Organoiron(II) compounds |
|
|---|
- Fe3O4
- Fe3S4
| Organoiron(III) compounds |
|
|---|
- FeF4
- K2FeO4
- BaFeO4













