Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| PCK1 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1KHB, 1KHE, 1KHF, 1KHG, 1M51, 1NHX, 2GMV |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PCK1, PEPCK-C, PEPEPCKC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1, PCKDC |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 614168; MGI: 97501; HomoloGene: 1944; GeneCards: PCK1; OMA:PCK1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 20 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 20q13.31 | Start | 57,561,080 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 57,568,121 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 2 H3|2 95.79 cM | Start | 172,994,841 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 173,001,066 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - jejunal mucosa
- right lobe of liver
- glomerulus
- metanephric glomerulus
- kidney tubule
- human kidney
- mucosa of colon
- renal medulla
- mucosa of sigmoid colon
- mucosa of ileum
|
| | Top expressed in | - right kidney
- brown adipose tissue
- human kidney
- left lobe of liver
- white adipose tissue
- subcutaneous adipose tissue
- tunica adventitia of aorta
- intercostal muscle
- mammary gland
- mesenteric lymph nodes
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 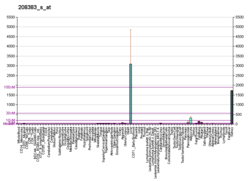 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - nucleotide binding
- manganese ion binding
- GDP binding
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity
- GTP binding
- metal ion binding
- carboxylic acid binding
- purine nucleotide binding
- lyase activity
- carboxy-lyase activity
- magnesium ion binding
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- cytosol
- extracellular exosome
| | Biological process | - glucose homeostasis
- internal protein amino acid acetylation
- lipid metabolism
- response to activity
- positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to acidic pH
- oxaloacetate metabolic process
- response to insulin
- glyceroneogenesis
- cellular response to potassium ion starvation
- cellular response to retinoic acid
- response to lipid
- cellular response to hypoxia
- cellular response to fructose stimulus
- response to interleukin-6
- glucose metabolic process
- human ageing
- response to methionine
- cellular response to interleukin-1
- cellular response to glucagon stimulus
- cellular response to cAMP
- cellular response to insulin stimulus
- cellular response to tumor necrosis factor
- response to lipopolysaccharide
- gluconeogenesis
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 20: 57.56 – 57.57 Mb | Chr 2: 172.99 – 173 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (soluble), also known as PCK1, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the PCK1 gene.[5][6]
Function
This enzyme is a main control point for the regulation of gluconeogenesis. The cytosolic enzyme encoded by this gene, along with GTP, catalyzes the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from oxaloacetate, with the release of carbon dioxide and GDP. The expression of this gene can be regulated by insulin, glucocorticoids, glucagon, cAMP, and diet. A mitochondrial isozyme of the encoded protein also has been characterized.[5]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
[[File:
|alt=Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis edit]]
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis edit
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "GlycolysisGluconeogenesis_WP534".
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000124253 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027513 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: PCK1 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (soluble)".
- ^ Pilz AJ, Willer E, Povey S, Abbott CM (October 1992). "The genes coding for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-1 (PCK1) and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit (CHRNA4) map to human chromosome 20, extending the known region of homology with mouse chromosome 2". Ann. Hum. Genet. 56 (Pt 4): 289–93. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1992.tb01155.x. PMID 1492743. S2CID 23586336.
Further reading
- Beale EG, Hammer RE, Antoine B, Forest C (2004). "Disregulated glyceroneogenesis: PCK1 as a candidate diabetes and obesity gene". Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 15 (3): 129–35. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2004.02.006. PMID 15046742. S2CID 9194909.
- Pilz AJ, Willer E, Povey S, Abbott CM (1993). "The genes coding for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-1 (PCK1) and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit (CHRNA4) map to human chromosome 20, extending the known region of homology with mouse chromosome 2". Ann. Hum. Genet. 56 (Pt 4): 289–93. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1992.tb01155.x. PMID 1492743. S2CID 23586336.
- Giralt M, Park EA, Gurney AL, et al. (1991). "Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Evidence for synergistic interaction between thyroid hormone and cAMP cis-regulatory elements". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (32): 21991–6. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)54735-9. PMID 1657985.
- Beale EG, Chrapkiewicz NB, Scoble HA, et al. (1985). "Rat hepatic cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Structures of the protein, messenger RNA, and gene". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (19): 10748–60. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85145-1. PMID 2993287.
- Ting CN, Burgess DL, Chamberlain JS, et al. (1993). "Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP): characterization of the human PCK1 gene and localization distal to MODY on chromosome 20" (PDF). Genomics. 16 (3): 698–706. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1250. hdl:2027.42/30779. PMID 8325643.
- Yu H, Thun R, Chandrasekharappa S, et al. (1993). "Human PCK1 encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is located on chromosome 20q13.2" (PDF). Genomics. 15 (1): 219–21. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1040. hdl:2027.42/31063. PMID 8432541.
- Stoffel M, Xiang KS, Espinosa R, et al. (1993). "cDNA sequence and localization of polymorphic human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene (PCK1) to chromosome 20, band q13.31: PCK1 is not tightly linked to maturity-onset diabetes of the young". Hum. Mol. Genet. 2 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1093/hmg/2.1.1. PMID 8490617.
- O'Brien RM, Printz RL, Halmi N, et al. (1996). "Structural and functional analysis of the human phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1264 (3): 284–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00194-8. PMID 8547315.
- Parissi V, Calmels C, De Soultrait VR, et al. (2001). "Functional interactions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase with human and yeast HSP60". J. Virol. 75 (23): 11344–53. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.23.11344-11353.2001. PMC 114720. PMID 11689615.
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. 414 (6866): 865–71. Bibcode:2001Natur.414..865D. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Dunten P, Belunis C, Crowther R, et al. (2002). "Crystal structure of human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase reveals a new GTP-binding site". J. Mol. Biol. 316 (2): 257–64. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5364. PMID 11851336.
- Jurado LA, Song S, Roesler WJ, Park EA (2002). "Conserved amino acids within CCAAT enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP(alpha) and beta) regulate phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) gene expression". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (31): 27606–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201429200. PMID 11997389.
- Wilson HL, McFie PJ, Roesler WJ (2003). "Different transcription factor binding arrays modulate the cAMP responsivity of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (46): 43895–902. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203169200. PMID 12237288.
- Borgius LJ, Steffensen KR, Gustafsson JA, Treuter E (2003). "Glucocorticoid signaling is perturbed by the atypical orphan receptor and corepressor SHP". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (51): 49761–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205641200. PMID 12324453.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Chakravarty K, Wu SY, Chiang CM, et al. (2004). "SREBP-1c and Sp1 interact to regulate transcription of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in the liver". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (15): 15385–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309905200. PMID 14744869.
- Cao H, van der Veer E, Ban MR, et al. (2004). "Promoter polymorphism in PCK1 (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene) associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89 (2): 898–903. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031361. PMID 14764811.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Hajarnis S, Schroeder JM, Curthoys NP (2005). "3'-Untranslated region of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA contains multiple instability elements that bind AUF1". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (31): 28272–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501204200. PMID 15951444.
PDB gallery
-
1khb: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, native data -
1khe: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, MAD data -
1khf: PEPCK complex with PEP -
1khg: PEPCK -
1m51: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor -
1nhx: PEPCK COMPLEX WITH A GTP-COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR -
2gmv: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor |
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 20 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |



 1khb: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, native data
1khb: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, native data 1khe: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, MAD data
1khe: PEPCK complex with nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, MAD data 1khf: PEPCK complex with PEP
1khf: PEPCK complex with PEP 1khg: PEPCK
1khg: PEPCK 1m51: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor
1m51: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor 1nhx: PEPCK COMPLEX WITH A GTP-COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR
1nhx: PEPCK COMPLEX WITH A GTP-COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR 2gmv: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor
2gmv: PEPCK complex with a GTP-competitive inhibitor

























