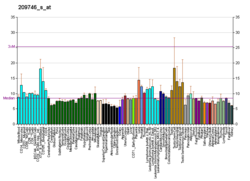
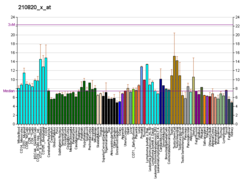
COQ7
| COQ7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identificadores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomes alternativos | COQ7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IDs externos | OMIM: 601683 HomoloGene: 6953 GeneCards: COQ7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Doenças Geneticamente Relacionadas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| coenzyme Q10 deficiency, primary, 8; COQ10D8[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A 5-desmetoxibiquinona hidroxilase mitocondrial (DMQ hidroxilase), também conhecida como coenzima Q7, hidroxilase, é uma enzima que em humanos é codificada pelo gene COQ7. O gene clk-1 (clock-1) codifica essa proteína necessária para a biossíntese de ubiquinona no verme Caenorhabditis elegans e outros eucariotos. A versão em camundongo do gene é chamada mclk-1 e o homólogo humano, mosca da fruta e levedura COQ7 (proteína de biossíntese da coenzima Q 7).[3][4]
Referências
- ↑ «Doenças geneticamente associadas a COQ7 ver/editar referências no wikidata»
- ↑ «Human PubMed Reference:»
- ↑ Ewbank JJ, Barnes TM, Lakowski B, Lussier M, Bussey H, Hekimi S (fevereiro de 1997). «Structural and functional conservation of the Caenorhabditis elegans timing gene clk-1». Science. 275 (5302): 980–3. PMID 9020081. doi:10.1126/science.275.5302.980
- ↑ «Entrez Gene: COQ7 coenzyme Q7 homolog, ubiquinone (yeast)»
 | Este artigo sobre Genética é um esboço. Você pode ajudar a Wikipédia expandindo-o.
|
Leitura adicional
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). «Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides.». Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. PMID 8125298. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). «Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library.». Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. PMID 9373149. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3
- Jonassen T, Proft M, Randez-Gil F, et al. (1998). «Yeast Clk-1 homologue (Coq7/Cat5) is a mitochondrial protein in coenzyme Q synthesis.». J. Biol. Chem. 273 (6): 3351–7. PMID 9452453. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.6.3351
- Asaumi S, Kuroyanagi H, Seki N, Shirasawa T (1999). «Orthologues of the Caenorhabditis elegans longevity gene clk-1 in mouse and human.». Genomics. 58 (3): 293–301. PMID 10373327. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5838
- Vajo Z, King LM, Jonassen T, et al. (2000). «Conservation of the Caenorhabditis elegans timing gene clk-1 from yeast to human: a gene required for ubiquinone biosynthesis with potential implications for aging.». Mamm. Genome. 10 (10): 1000–4. PMID 10501970. doi:10.1007/s003359901147
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). «DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination.». Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. PMC 310948
 . PMID 11076863. doi:10.1101/gr.143000
. PMID 11076863. doi:10.1101/gr.143000 - Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). «Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs.». Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. PMC 311072
 . PMID 11230166. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R
. PMID 11230166. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R - Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). «Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing.». EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. PMC 1083732
 . PMID 11256614. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058
. PMID 11256614. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058 - Stenmark P, Grünler J, Mattsson J, et al. (2001). «A new member of the family of di-iron carboxylate proteins. Coq7 (clk-1), a membrane-bound hydroxylase involved in ubiquinone biosynthesis.». J. Biol. Chem. 276 (36): 33297–300. PMID 11435415. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100346200
- Takahashi M, Asaumi S, Honda S, et al. (2001). «Mouse coq7/clk-1 orthologue rescued slowed rhythmic behavior and extended life span of clk-1 longevity mutant in Caenorhabditis elegans.». Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 286 (3): 534–40. PMID 11511092. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5439
- Rea S (2002). «CLK-1/Coq7p is a DMQ mono-oxygenase and a new member of the di-iron carboxylate protein family.». FEBS Lett. 509 (3): 389–94. PMID 11749961. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03099-X
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). «Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.». Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899 - Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). «Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.». Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. PMID 14702039. doi:10.1038/ng1285
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). «From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline.». Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. PMC 528930
 . PMID 15489336. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704
. PMID 15489336. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704 - Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). «The LIFEdb database in 2006.». Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. PMC 1347501
 . PMID 16381901. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139
. PMID 16381901. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139
 Portal da genética
Portal da genética Portal da bioquímica
Portal da bioquímica