| PSME4 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PSME4, PA200, proteasome activator subunit 4 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 607705; MGI: 2143994; HomoloGene: 113742; GeneCards: PSME4; OMA:PSME4 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 2p16.2 | Start | 53,864,069 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 53,970,993 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 11|11 A4 | Start | 30,721,726 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 30,830,361 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - sperm
- glutes
- gastrocnemius muscle
- left testis
- biceps brachii
- right testis
- Skeletal muscle tissue of biceps brachii
- deltoid muscle
- triceps brachii muscle
- vastus lateralis muscle
|
| | Top expressed in | - temporal muscle
- triceps brachii muscle
- vastus lateralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
- digastric muscle
- myocardium of ventricle
- gastrocnemius muscle
- spermatid
- medial head of gastrocnemius muscle
- cardiac muscles
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 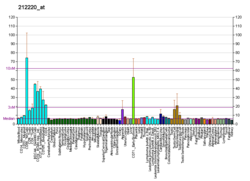

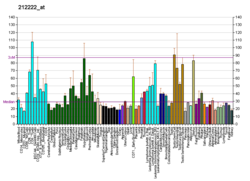 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- peptidase activator activity
- lysine-acetylated histone binding
- proteasome binding
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- nuclear speck
- proteasome complex
- nucleus
- nucleoplasm
- cytosol
- proteasome core complex
- spermatoproteasome complex
| | Biological process | - cell differentiation
- regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process
- antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I, TAP-dependent
- regulation of mRNA stability
- positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
- protein polyubiquitination
- stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
- MAPK cascade
- cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
- positive regulation of peptidase activity
- multicellular organism development
- Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway
- NIK/NF-kappaB signaling
- spermatogenesis
- anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
- DNA repair
- proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
- Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway
- proteasomal ubiquitin-independent protein catabolic process
- negative regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle
- protein deubiquitination
- SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process
- transmembrane transport
- regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia
- post-translational protein modification
- regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
- interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway
- regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 53.86 – 53.97 Mb | Chr 11: 30.72 – 30.83 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|



















